组件编程-类组件实例的props
props概念
- 每个组件对象都会有
props(properties简写)属性 - 每组标签的所有属性, 都保存在
props中
作用
- 通过标签属性, 从组件外部向组件内部传递变化的数据
注意
- 属性
props为只读, 不能从内部修改数据
编码规范
-
组件属性的限制, 包括类型, 必要性等
-
==React15.5弃用==( 需要引入
props-types.js库 )-
Person.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 类型字串, 必须包含
age: PropTypes.number, // 类型数字
}
-
-
==React15.5之前==
-
Person.propTypes = {
name: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 类型字串, 必须包含
age: React.PropTypes.number, // 类型数字
}
-
-
-
扩展属性: 对象所有的属性, 都通过
props传递-
<Person {...person}/>
-
-
组件属性的默认值
-
Person.defaultProps = {
age: 18,
sex:'男'
}
-
-
组件中的构造函数
-
如果==需要在构造器中通过
this访问props==, 则需要构造函数 -
constructor(props){
super(props)
console.log(props)//打印所有属性
}
-
-
组件内部读取属性值
this.props.name
案例: 显示人员信息的组件
需求: 自定义一个用来显示人员信息的组件
- 姓名, 性别, 年龄分别使用无序列表表示
- 姓名必须指��定, 且为字符串
- 性别字符串类型, 没有指定时默认为男
- 年龄为数字类型, 没有指定时默认18
基础框架实现
<script type="text/babel">
class Person extends React.Component{
render(){
// console.log(this)
const {name, age, sex} = this.props;
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名: {name}</li>
<li>性别: {sex}</li>
<li>年龄: {age+1}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="jack" sex="男" age={16}/>, document.getElementById("test"));
const test1 = {name:"black", sex:"男", age:22};
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...test1}/>, document.getElementById("test1"))
</script>
<Person {...test1}/>- 数组的展开运算符, 原本==不能直接展开对象==
- 在
js6语法中, 可以使用{...person}, ==表示copy对象== - 在当前
jsx+babel中, 直接使用…test1, ==表示对象展开==- 其中的
{}, 仅表示==语法隔离==
- 其中的
增加对标签属性的限制
<script type="text/babel">
class Person extends React.Component{
render(){
// console.log(this)
const {name, age, sex} = this.props;
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名: {name}</li>
<li>性别: {sex}</li>
<li>年龄: {age+1}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
Person.propTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 必须包含, 且为字符串
sex:PropTypes.string,
age:PropTypes.number,
speak:PropTypes.func,
}
Person.defaultProps = {
sex: "女",
age: 18
}
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="jack" sex="男" age={16}/>, document.getElementById("test"));
const test1 = {name:"black", sex:"男", age:22};
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...test1}/>, document.getElementById("test1"))
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="park" speak={speak}/>, document.getElementById("test2"));
function speak(){
console.log("我说话了")
}
</script>
简写props: 优化上述案例
static关键字: ==静态方法, 只能被类自身调用==
- 将
propTypes属性 &defaultProps属性变为类本身的静态属性
class Person extends React.Component{
static propTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 必须包含, 且为字符串
sex:PropTypes.string,
age:PropTypes.number,
speak:PropTypes.func,
}
static defaultProps = {
sex: "女",
age: 18
}
render(){
// console.log(this)
const {name, age, sex} = this.props;
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名: {name}</li>
<li>性别: {sex}</li>
<li>年龄: {age+1}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
类中构造器与props( 几乎不用 )
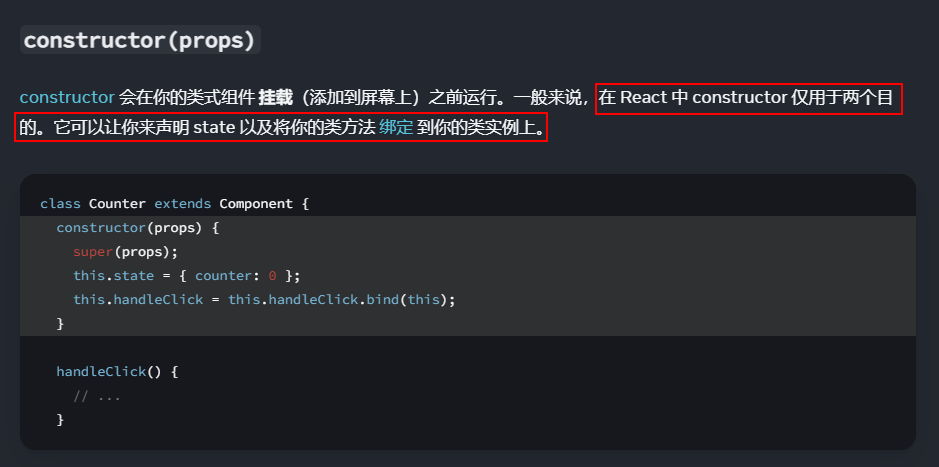
然而, 对于声明 state 我们可以直接在类中添加 state 属性
对于类方法绑定, 我们可以借助关键字 static
因此除了需要在构造器中通过 this 访问 props 以外, 我们==几乎不使用构造函数==